OVERVIEW
Led by researchers in the Speech, Language and Music (SLAM) Lab at UT Dallas, this EEG study explores the effects of binaural beats (BB) on language processing and neural oscillations. Generated by presenting slightly mismatched pure tones to each ear, BB have been suggested to enhance cognitive states. Researchers focused on frequencies, known for their potential cognitive benefits, building upon a previous behavioral study where participants who were exposed to beta and gamma BB demonstrated improved comprehension, especially when processing complex sentences. 60 participants helped explore these effects. Following a 10-minute stimulation phase, exposure to 18-Hz binaural beats resulted in significantly higher accuracy and faster response times during a comprehension task, particularly for complex sentences. Researchers continue to investigate the association between these improvements and attenuated beta power differences between sentence types. This paper's findings shed light on the neural mechanisms underlying the language-enhancing effects of BB at specific frequencies.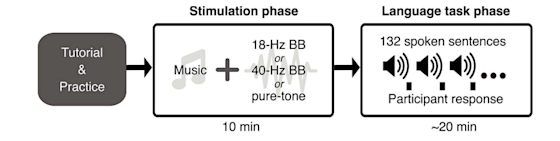
Figure 1. A schematic of the experimental procedure