Overview
Hemodynamic response function (HRF) characterizes the blood-oxygen-level-dependent (BOLD) signal of the brain over time through functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI). HRF can change over time as we age, and this is an important measurement in studies of the aging brain and its function. This study sought to use a large sample size to assess the HRF changes in healthy aging participants. The HRF was calculated in the visual, auditory, and motor cortices and there was found to be a significant difference for all three between older and younger participants. These neurovascular changes due to ages are relatively new findings, and further studies will continue to explore the implications of such discovery.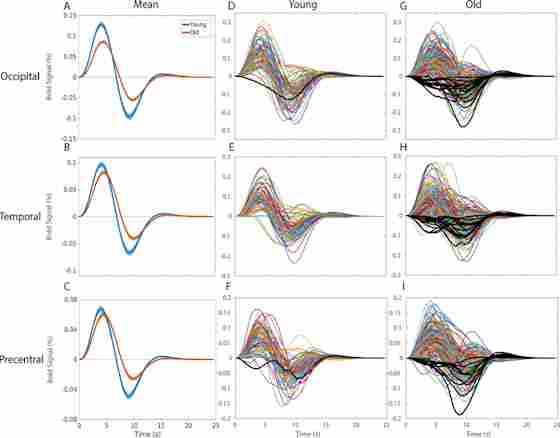
Figure 2. Hemodynamic Response Functions across (blue) young and (orange) healthy older adults in A) the occipital region of interest in response to a checkerboard stimulus for 34 ms, B) the temporal region of interest in response to 300 ms binaural tone at 1200 Hz, and C) the LH precentral region of interest due to right-index finger button-press response with the (solid line).



